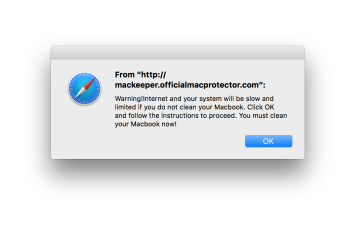
At this point there are quite significant increase in malicious browser plugins that displays ads without enough disclosure. Quite often their tracks are hidden and it is not so easy to remove them. The makers use 2 ways to start showing adware :
- Distributing plugins with bundles or trojans (aka “movie downloads”, etc).
- Purchasing popular plugins and releasing ad-supported versions.
While second way is almost legitimate, it is handled by browser makers effectively and is not so dangerous. Fast burning a plugin with significant user base is not something most adware makers want.
However, the makers of trojan – distributed adware plugins try to make sure their ads will be difficult to block permanently or tracked to their companies without caring about how long the plugin itself will last. Thus there is increase in CDNs supported popups. They are hard to block as the same infrastructure is used for legitimate content and pages.
What is CDN
CDN is short for content delivery network. These services help website load faster by keeping copies of website images and other static content in several locations around the globe. This helps a lot, and in majority of cases there are no reason not to use CDN for global websites.
The speedup is two-fold. Firstly, it the loaded content does not use main server. Secondly, it is automatically closer to the end-user and thus it loads much faster.
There are plenty of CDNs to choose from. The most popular ones are cloudflare (which helps with website page caching as well), Amazon’s cloudfront, to some extent Amazons AWS, AkamaiHD and several more. All of them were used by advertising networks at some point. More about CDNs in general and their list is available on Wikipedia. Personally, I use Cloudfront for some of my sites.
Why malware makers use CDN
Malware makers use CDN for the same reason as legitimate users: They need to show content faster, reduce load on their own servers. Additionally, they have one more reason: it helps them avoid blockage from various antivirus applications.
Many antivirus applications will block blacklisted domains and does can’t blacklist whole content delivery network at once. They have to rely on blacklisting various patterns which can be changed faster than changing domains and servers. Thus some of CDN-delivered malicious content will be shown to end user even if it has decent malware blocking program.
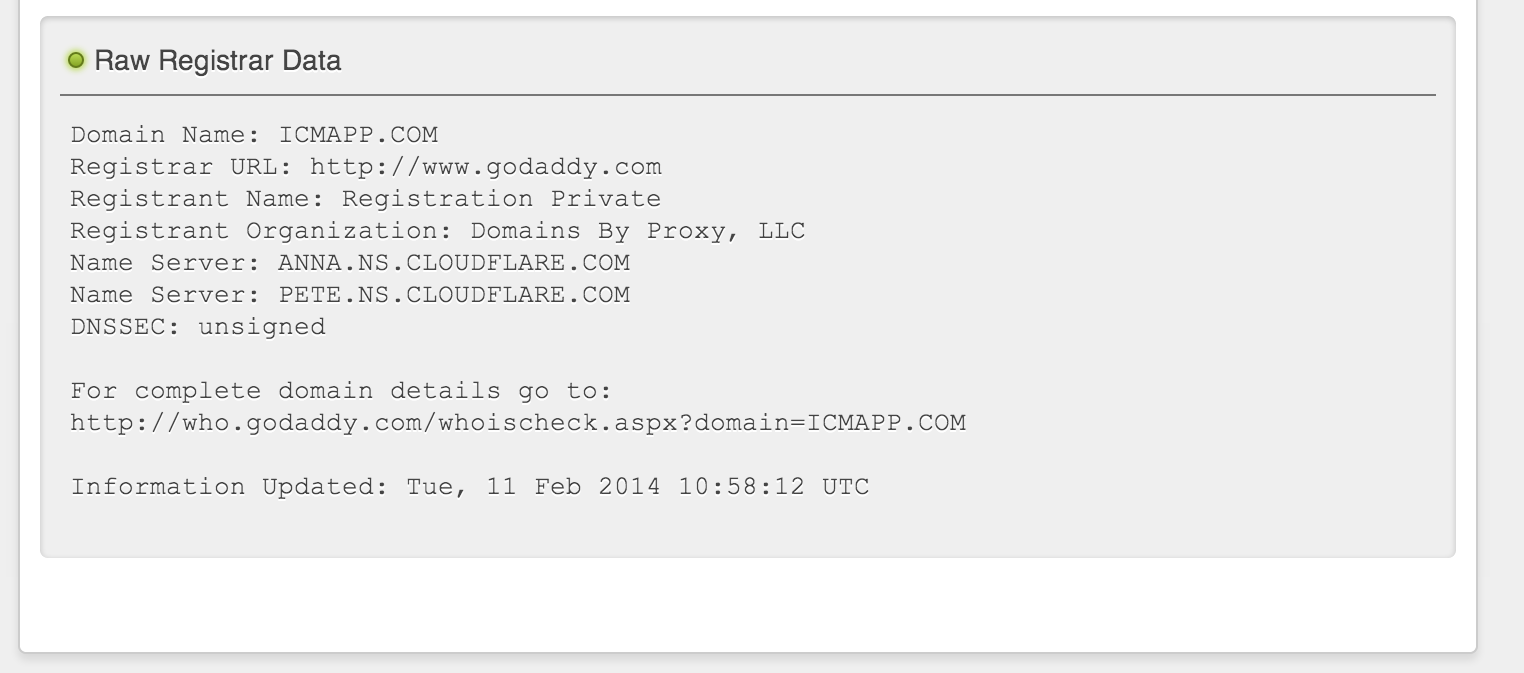
As and example, lets look at static.icmapp.com – a domain having huge Alexa rating ( ~6500). � The registration is private and the DNS services are ones of cloudflare – webpage acceleration network. Lots of legitimate pages use it, so it is not possible to block sites by IP that easily. I think it is used in Plus-HD plugin family that is made for advertising only.
They haven’t bothered to set up real page at all. icmapp main domain is godaddy parking page. Some advertising networks care enough to provide some placeholder to explain themselves. Not so in this case.
What happens now? First, even if the domain will be blocked it is quite easy to launch other domains under same (or different) name under cloudflare without bigger changes to infrastructure. There won’t be a need to change icmapp com mains servers as they are not visible for end user. Even if they are kicked, there won’t be enough checks to make sure such thing won’t happen again.
There is still hope that majority of browsers will change the way plugins get installed and perform checks for installed non-market plugins. This would be privacy risk, but would solve issue with malicious advertisings once and for all.
Currently, browsers try to limit plugins to the ones available in their public repositories. This reduces amount of malicious plugins but does not solve problems fully.



0 Comments